Exam to See How Baby Is in Uterus
Mutual Tests During Pregnancy
These are some of the more common tests done during pregnancy.
Outset trimester prenatal screening tests
First trimester screening is a combination of fetal ultrasound and maternal blood testing. Information technology can help find out the risk that the fetus has sure birth defects. Screening tests may be used alone or with other tests.
Starting time trimester screening has 3 parts.
Ultrasound test for fetal nuchal translucency (NT)
Nuchal translucency screening uses an ultrasound test to check the area at the dorsum of the fetal neck for extra fluid or thickening.
Two maternal serum (blood) tests
These tests measure 2 substances found in the blood of all significant women:
-
Pregnancy-associated plasma protein screening (PAPP-A). This is a protein made past the placenta in early on pregnancy. Aberrant levels are linked to a higher adventure for chromosome bug.
-
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This is a hormone made past the placenta in early on pregnancy. Abnormal levels are linked to a college take a chance for chromosome bug.
When used together, these tests have a greater ability to discover out if the fetus might have a genetic nascency defect such every bit Down syndrome (trisomy 21) and trisomy xviii.
If the results of these tests are abnormal, your healthcare provider volition advise genetic counseling. You lot may need more testing. That may include chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis, cell-free fetal Deoxyribonucleic acid, or other ultrasounds.
2d trimester prenatal screening tests
Second trimester prenatal screening may include several blood tests. These are called multiple markers. They requite information about a woman's hazard of having a baby with certain genetic conditions or nascency defects. Screening is ofttimes done by taking a sample of your blood between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy. The 16th to 18th is ideal. The multiple markers are listed below.
Alpha-fetoprotein screening (AFP)
This blood test measures the level of alpha-fetoprotein in your blood during pregnancy. AFP is a protein normally made by the fetal liver. It is in the fluid around the fetus (amniotic fluid) and crosses the placenta into your blood. The AFP blood exam is too called MSAFP (maternal serum AFP). Abnormal levels of AFP may be a sign of:
-
Open up neural tube defects (ONTD) such every bit spina bifida
-
Down's syndrome
-
Other chromosome problems
-
Bug in the abdominal wall of the fetus
-
Twins. More than one fetus is making the protein.
-
An incorrect due date. The levels of AFP vary throughout pregnancy.
Other markers
Other markers are:
-
hCG. This is man chorionic gonadotropin hormone. It is fabricated past the placenta.
-
Estriol. This is a hormone made past the placenta.
-
Inhibin. This is a hormone fabricated by the placenta.
Abnormal results of AFP and other markers may mean you lot need more than testing. An ultrasound is often done to confirm the dates of the pregnancy. It also looks at the fetal spine and other body parts for issues. You may need an amniocentesis for accurate diagnosis.
Multiple mark screening is non diagnostic. This means information technology is not 100% authentic. Information technology is simply a screening test to find out who should be offered more testing for their pregnancy. The tests show false-positive results. This means they show a trouble when the fetus is actually salubrious. Or the results may be faux negative. This means they prove that the fetus is normal when the fetus really does take a health trouble.
Having both offset and 2nd trimester screening tests washed makes it more likely to discover a problem, if there is one, than using just 1 screening lonely. As many as nineteen out of 20 cases of Down syndrome can exist plant when both showtime and second trimester screening are used.
What is an amniocentesis?
An amniocentesis is a test that takes a small sample of the amniotic fluid. It is done to diagnose chromosome problems and open neural tube defects (ONTDs) such equally spina bifida. The test tin too look for other genetic bug and disorders if y'all have a family history of them. These other results as well depend on the lab doing the testing. An amniocentesis is mostly offered to women between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy who are at higher gamble for chromosome problems. This includes women who take had an abnormal maternal blood screening test. The test may accept indicated a higher risk for a chromosome problem or neural tube defect.
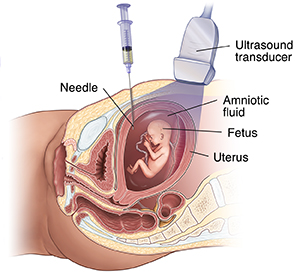
How is an amniocentesis done?
An amniocentesis involves putting a long, sparse needle through your belly into the amniotic sac. The healthcare provider withdraws a pocket-size sample of the amniotic fluid. The amniotic fluid has cells shed by the fetus. These cells accept genetic data. The specific details of each test vary slightly, but an amniocentesis ofttimes follows this process:
-
The healthcare squad cleans your belly (abdomen) with an clarified.
-
The healthcare provider may use a local anesthetic to numb the skin.
-
The provider uses ultrasound to help guide a hollow needle into the amniotic sac.
-
The provider withdraws a small sample of fluid to be sent to a lab.
After the test, don't do any strenuous activeness for 24 hours. Y'all may feel some cramping during or after the amniocentesis.
If you are carrying twins or other multiples, you will demand sampling from each amniotic sac to study each baby.
The fluid sample is sent to a genetics lab then that the cells tin grow and exist tested. AFP is also measured to dominion out an open neural tube defect such as spina bifida. AFP is a poly peptide fabricated past the fetus and is in the fluid.
Results are often available in ten days to 2 weeks, depending on the lab.
Talk over the risks of this procedure with your healthcare provider. Sometimes the amniocentesis can't be done. It depends on the position of the baby, the placenta, the amount of fluid, and your beefcake.
What is a chorionic villus sampling (CVS)?
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a prenatal test. It involves taking a sample of some of the placental tissue. This tissue often has the same genetic fabric as the fetus. It can exist tested for chromosome bug and some other genetic problems. The examination tin also look for other genetic problems and disorders if you take a family history of them. These other results also depend on the lab doing the testing. Dissimilar amniocentesis, CVS does not requite information on neural tube defects such as spina bifida. For this reason, women who have CVS also need a follow-up blood test between 16 and xviii weeks of their pregnancy to screen for neural tube defects.
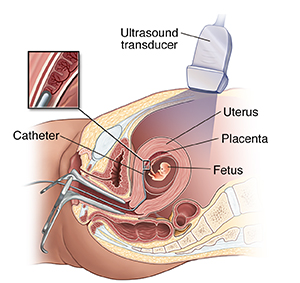
How is CVS done?
CVS may be offered if you are at higher take chances for chromosome problems. You may as well exist offered it if yous have a family history of a genetic trouble that is testable from the placental tissue. CVS is usually done between the 10th and 13th weeks of pregnancy. The verbal method for CVS can vary, but the procedure involves putting a pocket-sized tube (catheter) through your vagina and into your neck. Information technology usually follows this process:
-
The healthcare provider uses ultrasound to guide the catheter into place almost the placenta.
-
The provider removes tissue using a syringe on the other cease of the catheter.
-
For a transabdominal CVS, the provider puts a needle through your belly and into the uterus to take a sample of cells from the placenta.
-
Y'all may feel some cramping during and afterwards the CVS procedure.
If you are carrying twins or other multiples, you ofttimes will demand sampling from each placenta. But CVS is not always advised for multiples because the procedure is complicated and the placentas may not be in a adept position to get a sample.
The tissue samples are sent to a genetic lab to grow and be tested. Results are frequently available in 10 days to 2 weeks, depending on the lab.
Some women may non be candidates for CVS, or they may not go results that are 100% accurate. They may need a follow-upwards amniocentesis. In some cases, an active vaginal infection such as herpes or gonorrhea will prohibit the procedure. Other times, the healthcare provider takes a sample that does not have enough tissue to grow in the lab. That may cause incomplete or inconclusive results.
Hash out the risks of CVS with your healthcare provider.
What is fetal monitoring?
During late pregnancy and during labor, your healthcare provider may want to watch the fetal heart rate and other functions. Fetal heart rate monitoring is a way of checking the charge per unit and rhythm of the fetal heartbeat. The average fetal middle rate is between 110 and 160 beats per minute. It may modify every bit the fetus responds to conditions in the uterus. An aberrant fetal heart rate or blueprint may mean that the fetus is not getting plenty oxygen or there are other problems. Information technology also may hateful that an emergency or cesarean delivery is needed.
How is fetal monitoring done?
The most bones type of fetal heart rate monitor is to utilize a type of stethoscope called a fetoscope. Some other blazon of monitoring is with a hand-held Doppler device. This is oft used during prenatal visits to count the fetal center rate. During labor, continuous electronic fetal monitoring is often used. The specific details may vary slightly, but electronic fetal monitoring often follows this process:
-
The healthcare provider puts gel on your abdomen to assist the ultrasound transducer work properly.
-
The provider attaches the ultrasound transducer to the abdomen with straps and sends the fetal heartbeat to a recorder. The fetal centre rate is displayed on a screen and may exist printed onto special newspaper.
-
During contractions, a monitoring device (external tocodynamometer) is placed over the top of the uterus with a belt. This device can record the patterns of contractions.
Sometimes, internal fetal monitoring is needed for a more authentic reading of the fetal eye rate. This monitoring tin can be done when birth is close. Your amniotic sac must be broken, and your cervix must be partially dilated to do it. Internal fetal monitoring involves putting an electrode through the dilated neck. The electrode is attached to the scalp of the fetus.
What are glucose tolerance tests and the glucose challenge?
The kickoff 1-60 minutes test is a glucose claiming test. If the results are abnormal, a glucose tolerance test is done.
A glucose tolerance examination is often done in weeks 24 to 28 of pregnancy. Information technology measures levels of saccharide (glucose) in your claret. Abnormal glucose levels may be a sign of gestational diabetes.
How is a glucose tolerance exam done?
The glucose tolerance test is done if you lot have an elevated 1-hour glucose challenge test.
The specific details may vary slightly, but a glucose tolerance test oft follows this procedure:
-
You may exist asked to drink merely water on the day you get the test.
-
The healthcare provider will draw a fasting sample of blood from a vein.
-
You will be given a special glucose solution to drinkable.
-
The provider will draw claret several times over several hours to measure the glucose levels in your trunk.
What is a grouping B strep civilisation?
Grouping B streptococcus (GBS) are bacteria constitute in the lower genital tract of about one in four women. GBS infection oftentimes causes no issues in women earlier pregnancy. But it can crusade serious illness in the female parent during pregnancy. GBS may cause chorioamnionitis. This is a severe infection of the placental tissues. It can too crusade postpartum infection. Urinary tract infections acquired past GBS tin can lead to preterm labor and birth, or pyelonephritis and sepsis.
GBS is the most common cause of life-threatening infections in newborns, including pneumonia and meningitis. Newborn babies get the infection during pregnancy or from the mother'southward genital tract during labor and birth.
The CDC advises that all pregnant women exist screened for vaginal and rectal group B strep between 35 to 37 weeks gestation. If you lot have sure risk factors or a positive event, you should exist treated with antibiotics. This will lower the risk of passing GBS to your baby. Babies whose mothers become antibiotics for a positive GBS test are 20 times less probable to develop the affliction than those whose mothers don't get treatment.
What is an ultrasound?
An ultrasound browse is a test that uses high-frequency sound waves to make pictures of the internal organs. A screening ultrasound is sometimes washed during a pregnancy to check normal fetal growth and make sure of the due date. Ultrasounds may be washed at various times throughout pregnancy for many reasons.
In the first trimester
-
To detect out the due date. This is the near authentic mode of finding the due date.
-
To notice out the number of fetuses and see the placenta(s)
-
To diagnose an ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage
-
To look at the uterus and other pelvic anatomy
-
In some cases to observe fetal problems
Mid-trimester (sometimes chosen the eighteen- to 20-week scan)
-
To confirm the due date. A due engagement set in the offset trimester is rarely changed.
-
To observe out the number of fetuses and look at the placentas
-
To help with prenatal tests such every bit an amniocentesis
-
To look at the fetal beefcake to see if in that location are whatsoever problems
-
To check the amount of amniotic fluid
-
To wait at blood flow patterns
-
To sentinel fetal beliefs and action
-
To look at the placenta
-
To measure the length of the cervix
-
To check fetal growth
Tertiary trimester
-
To check fetal growth
-
To check the amount of amniotic fluid
-
To consummate a biophysical contour
-
To find out the position of a fetus
-
To check the placenta
How is an ultrasound scan done?
The specific details may vary slightly, just ultrasounds ofttimes follow the same process. Ii types of ultrasounds can exist done during pregnancy:
-
Intestinal ultrasound. In an abdominal ultrasound, the healthcare provider puts gel on your abdomen. The ultrasound transducer glides over the gel to create the image.
-
Transvaginal ultrasound. In a transvaginal ultrasound, the provider uses a smaller ultrasound transducer. They put the transducer into the vagina and rest it against the back of the vagina to create an image. A transvaginal ultrasound makes a sharper image. Information technology is ofttimes used in early pregnancy.
In that location are several types of ultrasound imaging techniques. The most common is 2-D. This gives a flat picture of one aspect of the image.
If more than information is needed, a iii-D ultrasound exam can be washed. This technique gives a 3-D moving picture. It requires a special car and special grooming. But the 3-D image lets the healthcare provider see width, superlative, and depth of images. These tin can be helpful in diagnosis. The iii-D images can likewise be saved for later review.
The latest engineering science is 4-D ultrasound. It lets the healthcare provider run across the fetus moving in existent time. With four-D imaging, a three-D image is continuously updated. This makes a "live activeness" view. These images often have a gilded color that helps testify shadows and highlights.
Ultrasound images may be captured in still photographs or on video to document findings.
Ultrasounds are constantly being improved and refined. As with whatsoever test, results may not be completely authentic. Just ultrasound can give valuable information for parents and healthcare providers to help manage and intendance for the pregnancy and fetus. Ultrasound too gives parents a special chance to come across their baby before birth. This helps them to bond and constitute an early relationship.
What are the risks and benefits of ultrasound?
Fetal ultrasound has no known risks other than mild discomfort. This is because of pressure from the transducer on the abdomen or in the vagina. No radiation is used during the process.
Transvaginal ultrasound requires that the ultrasound transducer be covered in a plastic or latex sheath. This may cause a reaction in women with a latex allergy.
Fetal ultrasound is sometimes offered in nonmedical settings to give keepsake images or videos for parents. The ultrasound procedure itself is considered safe, but it'due south possible that untrained workers may give parents false assurances about their infant'south well-beingness. Or perhaps a problem may be missed. Having ultrasound done by trained medical staff who can correctly understand findings is recommended. Talk with your healthcare provider or midwife if you lot have questions.
What is genetic carrier screening?
Many genetic bug can exist diagnosed before birth. Your healthcare provider or midwife may advise genetic testing during the pregnancy if yous or your partner accept a family history of genetic disorders or y'all have had a fetus or babe with a genetic problem.
Examples of genetic disorders that are commonly screened for include:
-
Cystic fibrosis
-
Spinal muscular dystrophy
-
Frail X
-
Thalassemia
-
Sickle jail cell anemia
-
Tay-Sachs disease
albrittonshase1964.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=85&contentid=p01241
0 Response to "Exam to See How Baby Is in Uterus"
Publicar un comentario